Real Life Systems Design: Notes
Slack architecture
Database
- PHP web app delivers a payload with websocket URL, hash indicating when delivered, database shard for particular team
- DB sharded by team, main DB keeps track of team -> shard relation. Multiple replicated DBs for main and shards
- main database:
SELECT db_shard FROM teams WHERE domain = %domain - team specific shard:
SELECT * FROM channels WHERE team_id = 711
- main database:
- Master-master replication so that writes can always go through, even if one master is down. How to handle duplicate/conflicting writes? Teams configured to write to one master only (even numbered teams write to masterA, odd to masterB), if master fails then switch.
- Memcache for certain queries
Message Server (web socket)
- Message server opens web socket connection with client. Also holds a 30 second buffer of messages to deliver once client joins web socket (if messages have been delivered between payload delivery and web socket connection)
- Also persists messages by writing to DB
Async job queue
- Redis job queue for certain operations (link unfurling, search indexing, importing messages)
NFRs/Bottleneck solutions
Availability thru rate limiting guards in front of key services
Monitor message queue depth in message server
Master-master replication
Shard DB by team
Vitess: Horizontally scale MySQL (shard) without dealing with sharding logic in application
Challenges
- Mains DB failure
- Quadratic relationship between members, teams, channels impacting start payload
Instagram Architecture
- Postgres, Django, Memcache one part of stack
- Interesting issue around cache invalidation with multi-datacenter replication
- When a write comes to the DB in one datacenter, have to use postgres replication mechanism and daemon to invalidate the cached key in both datacenters semi-concurrently. Previously, had Django setting the memcache key in one DC, not updated in the other
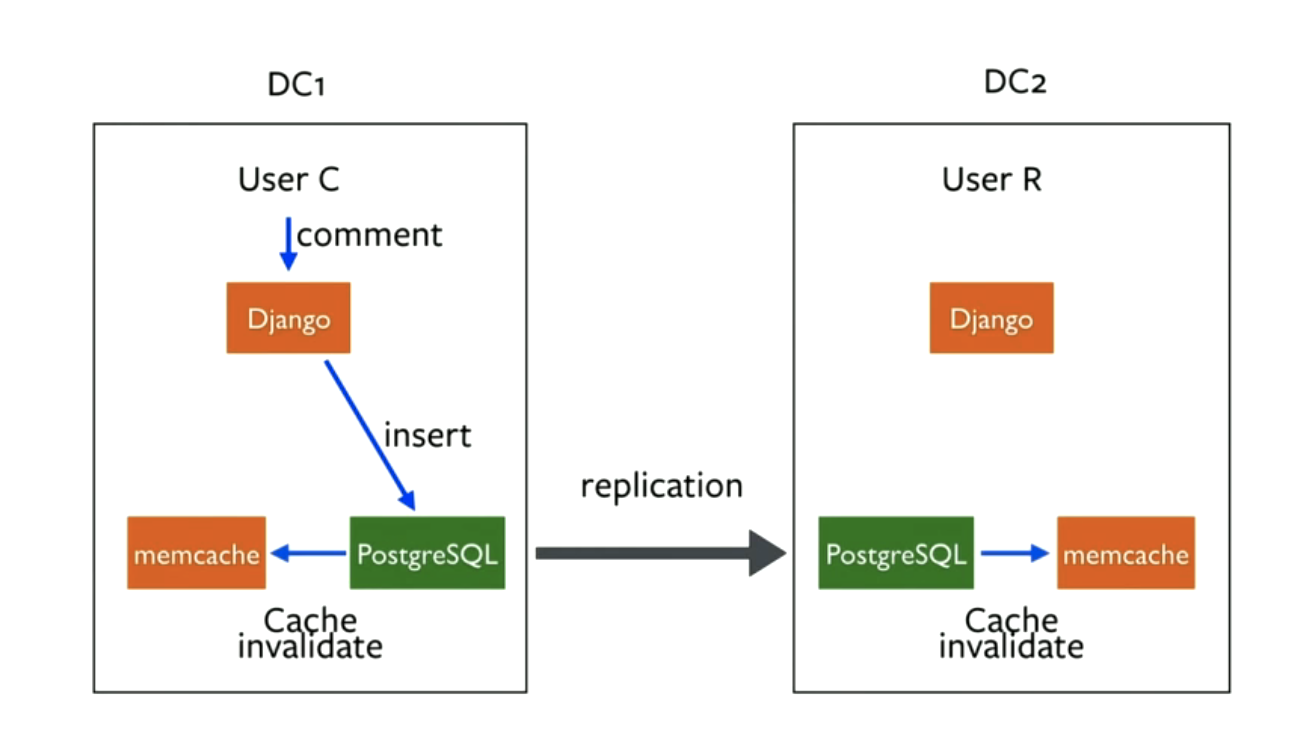
How to handle increased read load on DB when cache is invalidated across multiple datacenters? For certain features (like counts for popular posts), this data will have to be denormalized and stored in a separate table (avoid SELECT COUNT(*))
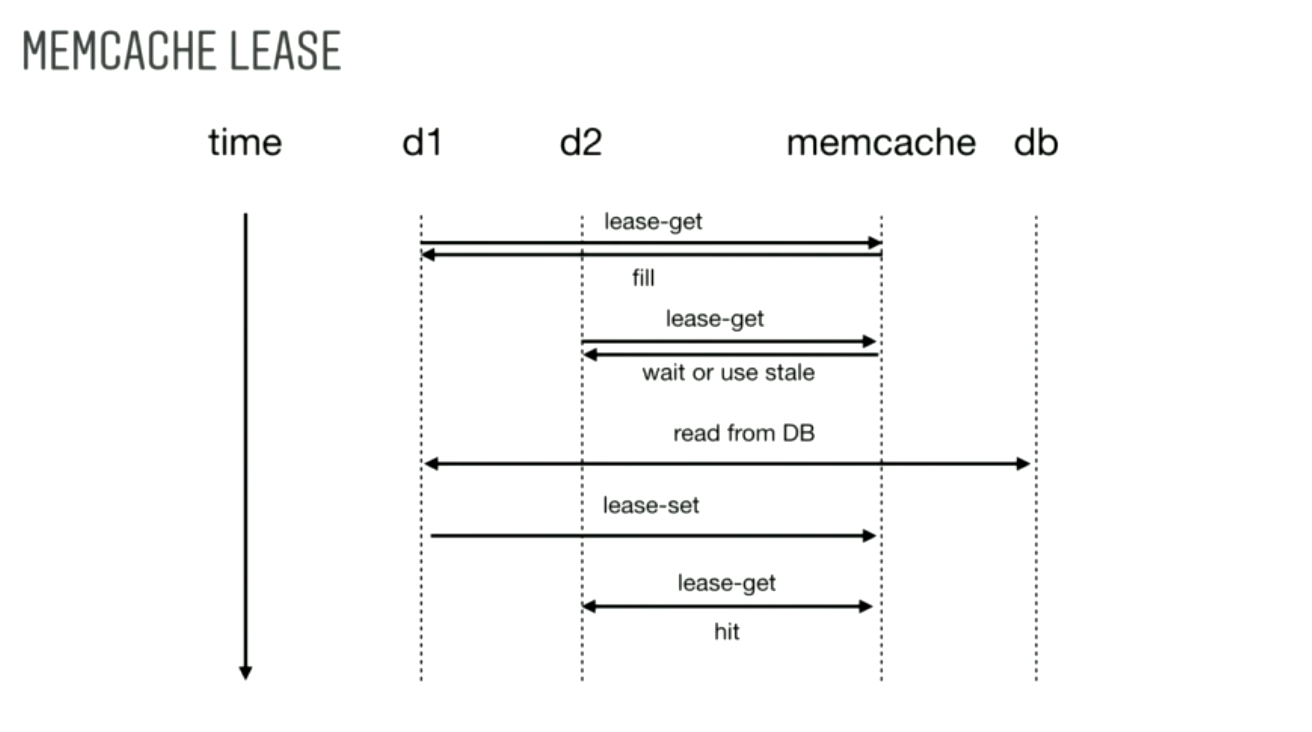
Even when stored in a separate table or DB like cassandra, will hit the cache a lot. So instead of letting tons of requests come in at the same time and read from the DB if the cache key is still stale, use a cache-lease. The first request to the cache will get a lease to go to the DB. Any subsequent requests will either get a stale result or can wait until the cache is updated.
Mentioned batching writes - gives control over writing to the DB. Can implement a simple queue, when it reaches a certain length, write to the DB
Twitter Feed Architecture
- Hybrid approach to solving for high read AND high write throughput.
- Pre-computed feed for each user based on follows.
- Event stream type system for updating user feeds when follows post a tweet
- For users with millions of followers, to avoid millions of writes, don’t update follower feeds
- Instead retrieve those users tweets at read time
Pinterest Architecture
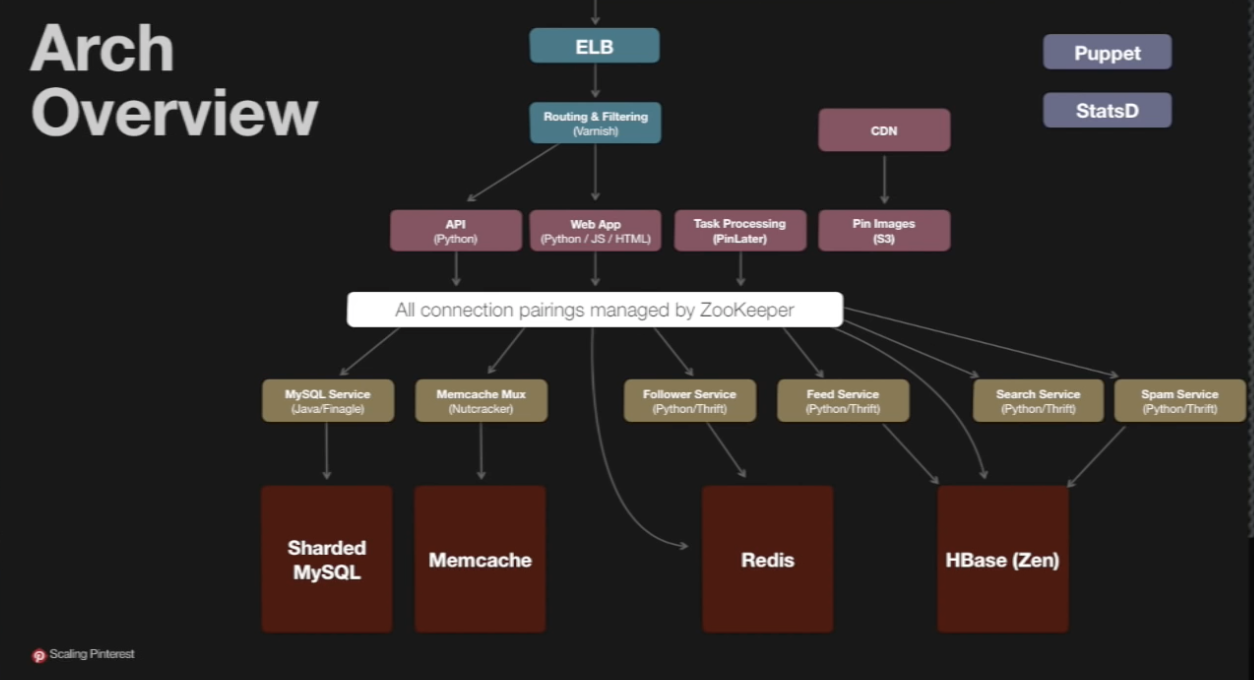
Redis
- Varieties of persistence options: now (write to disk immediately), snapshot, never
- Used at Pinterest both as cache and persistent storage
- Used for public feed storage (like Facebook graph) INSTEAD of MySQL because to insert in MySQL, have to walk a tree (B tree), whereas with feeds, a better data structure is a FIFO queue (most recent tweets/pins)
- True ordered list, O(1) insert
NoSQL generally
- Used for counters and search
Zookeeper
- Used for configuration management/service discovery - which box is where
Have to be aware of issues with read replicas. Sharding is preferred solution
- With read replicas, if write comes in, clears cache, and a subsequent request comes in before the new write is replicated to the read replica, the value will be stale (bug)
Financial Exchange (LMAX) (2020)
NFRs
- Throughput: 1 million transactions per sec
- Latency: 10s of microseconds
Concepts
- replicated state machines
- all nodes receive inputs in same order, execution is deterministic (iterating over keys in a map not deterministic)
- distributed event log best way to achieve this
- timestamps
- timestamped network packets
- priority heaps, timer wheels to handle multiple timers. Inject timestamp into event flow
- gateways
- typically markets had multiple gateways for clients/traders to connect to, but this was flawed
- clients would connect to all gateways to find ones with best execution time
- then submit unfillable orders at other gateways to flood traffic
- only one gateway is used
- now only one gateway per class of service
- multiple matching engines
- shard by asset class: equities (large or small), fx
- replicated state machines
Deployment
- continuous delivery
- automation
- test suites
- fast feedback cycles
- 24 * 7 operations
- snapshots of state
- quorums to be able to restart nodes
- monitoring
- flexible scaling
- be able to run entire stack on laptop or datacenter
- try to be able to run on one machine with IPC (machines are 100 core now)
- continuous delivery
Netflix Push Messaging
Maintain open websocket connections with 10s of thousands of machines Key notes:
- connection closing
- avoiding thundering herd